Introduction
The traditional pomotion strategy is not real time and almost rule based (might be implemented using automata by SW engineers in some technological companies).
The marketing pomotion has two kinds of effects:
- get more customers in
- get less of them out
In general, financial department will reserve specific amount of budget based on the coorperation’s monetory policies when a marketing compaign arrives. I summarised that the traditional promotion happens either by broadcasting to a broad group of consumers or tagging a broad group of commodities (labor, products,servcies), then present them to the customers. We say that they run in Dual Channel: Membership and Market Promotion by Displaying channel. We will go back to the definition above for details to witness how we build our fantastic models and systems step by step.
传统的促销策略,不是实时的,而且是规则化的(某些科技公司可能会雇佣SE用自动机去实现它)。通常,财务部门会在提案到达时,根据财政政策,分析并预留一定的预算。我总结,传统促销,“要么是以广播的形式发到目标群体消费者,要么是标记在商品(人力,产品,服务)上”。我们称,他们在“双渠道下运行”:会员渠道和展示促销渠道。稍后,我们将重新返回以上定义,见证我们如何一步一步构建我们神奇的系统和模型。
促销无外乎两种结果:
- 纳新
- 留存
In digital era, platforms gain a greate inevitable advantage over traditional manufactuers, consultants, service agents with respect to huge amount of ocean data and real time updating. If they are produced, collected, and consumed properly, and that be presented in front of customers in time, we can show the company how their promotion budget affects their income in fine scale, which can saves billion of dollars or even more for a big company.
数字时代,平台相对于传统的,制造、咨询以及服务商,有着不可逆转的巨大优势,就是海量数据和实时性。如果这些数据,被恰当地生产、收集和消费,并在客户恰好出现时用于促销服务,我们就可以向公司展示,他们的预算,是如何地,细致地帮助公司挣钱。这可是能省掉数十亿美元的经费!并且双赢。
The dual channel (as we talked here) of real time (what is constrained) promotion (a serious problem) targeting (in this post it is our target) is extremely challenging under symmetric infomation(participants orgnaized to refuse exchanges and wait for more promotion and fees triggered by system). Hence it is easier to assume that the marketing promotion activity is under asymmetric infomation(it is not too hard for a company to have secrets).
双渠道实时促销定向,在信息对称下,尤其困难(比如有规模的拒绝参与交易,触发哄抬物价或者调低折扣的,非正常消费、服务的抱团行为),所以我们会假定在非信息对称下(拥有秘密对于公司并不难)进行市场促销活动。
Domestic and international mathematical research on dual channel prices game can be traced back to Study on cooperation strategy between electronic channels and retailers in dual-channel supply chain, Chongqing University, 2007~2009, Price competition between retailers and manufacturer-owned stores, University of California at Berkeley, 2002. Later in 2010 researchers introduced stochastic infomation into the above models. Those methods are limited to classic economic models structure and not practical in real world because the quantities relationships are oversimplied.
“双渠道博弈”在国内的研究,国外的研究最早可以追溯到Study on cooperation strategy between electronic channels and retailers in dual-channel supply chain, Chongqing University, 2007~2009, 以及Price competition between retailers and manufacturer-owned stores, University of California at Berkeley, 2002。 后面在2010年,研究者给上述模型引进了,随机性。这些方法受限于经典经济学模型的结构和并且在数量关系上过于简单,并不适用于真实世界。
At the meantime, RTP is really different from Real Time Bidding (RTB) system. Speaking shortly, as you can see from picture below, RTP replaces bidding process with negotiation process.
同时,RTP和实时竞价(RTB)很不一样。简单地说,就像你从下图看到的一样,RTP将bidding环节,用“negotiation”环节代替了。
And once again, the model is defnitely in Stackelberg process. But it doesn’t matter at all, because we don’t have concepts of Stackelberg or Bertrand competitions inside model. We are in REAL TIME.
而且,模型是集中控制模式的。不过它并不重要,因为我们模型没有Stackelber竞争或者Bertrand竞争这种概念。我们是实时的。
This post will describe key concepts & notations RTP involves followed by describing system architecture in Chapter System Framework. Later we will give optmizers automata used inside system. Previous personal industry practices also indicate that multi-layer system is far more stable and reliable than one truely big End2End model of deep feature maps. Hence I will build model in that manner. I also realize that if the model is flexible and easy to control (interactively), it might help to relieve operation teams of a burdon of Agile Market Management (AMM).
这篇博文,首先会描绘RTP涉及的概念,然后在系统结构一章,描述系统结构。后面我会给出系统使用的优化器自动机。之前个人的工业项目实践,还表明,多层次系统比端到端系统更稳当和可信。因此系统是用优化器自动机方式构建。我同时意识到,如果模型足够灵活地方便配置,会极大地方便运营团队进行市场的敏捷管理(AMM).
Concepts Analysis
Real Time Promotion (RTP)
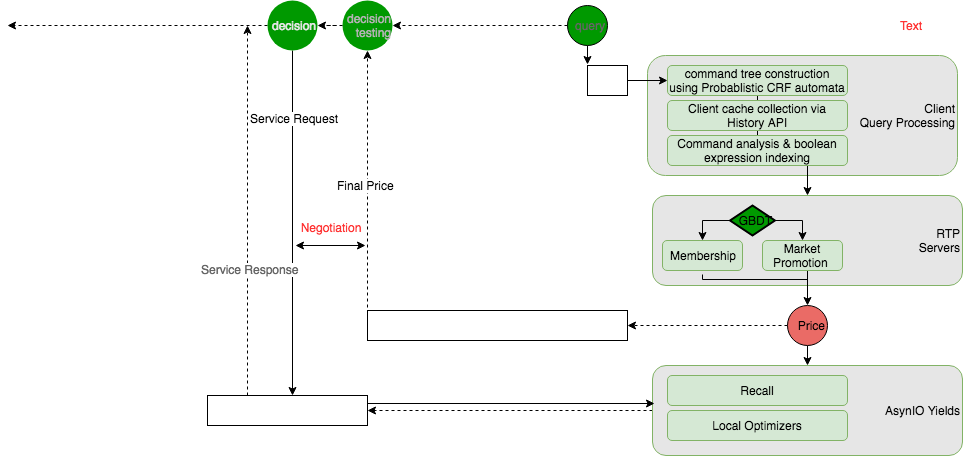
To understand RTP better, we must understand its business context:Upstream and Downstream. Usually RTP is between Recall and service optimizers. That is RTP will sometimes act as a selector to select possible customers into the next stage – preferred customer, obtaining higher dedcution offer.
为了更好地理解RTP,我们需要了解一些基本的业务上下游。通常RTP位于召回和服务优化器之间。因此RTP有时候会作为一个选择器,将顾客刷选进下一阶段:受到偏爱的顾客,可以获得更高的补贴提供。
For example, if I have limited products for sale,for a query from a customer who is not in membership, I need to calculate instant deduction based on marketing promotion budget. The decision making process is real time. First I will ask, have you used our products before? Second, why do you want it now (is it rigid demand?) and what really attracts you? Third, I might ask how much you would like to buy?
比如,如果我只有有限的产品,可供出售。对于一个并不是会员的询价请求,我会根据预算算出一个即时补贴。决策过程是实时的。我会询问这些问题:您用过我们的产品吗?是现在就要呢,还是稍后,是什么吸引您?我还会问,大概需要多少?
The decisoin process is complex I will make it easier for you to understand. Suppose you have price-sensitivity curve for this customer or if you don’t have,instead, you can estimate one from similar customers, then you got $I_{i}(v, k_{i}^{j}, u)$ for differnt observed $k_i^j$. Your budget can be $0$, which means you must earn some money. The price deduction is bounded by your budget and other conditions:
这个决策过程并不简单。我会然您更容易去理解。假定我们已经得到了每个顾客“价格-敏感度”曲线,如果没有,那就用数据估算。每个观测折扣$k_i^j$有$I_{i}(v, k_{i}^{j}, u)$。你的预算可能是$0$,也就说一定得挣点钱。
Customers
In market, customers can be aggreated by different types of demands. The demand is of genres:
市场中用户需求有以下分类:
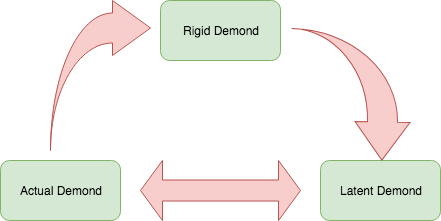
Rigid Demand
Their demands of some comodities are less affected by price or other benefits, and they are mostly VIPs or in memberships. They are not applicable to the marketing promotion which reduces total profit they contribute. Instead, they will be awarded based on membership policies. Sometimes membership benefits might be much larger than marketing promotion, but they are totally under control. This is part of practical demand.
他们对商品的需求,较少地收到价格、或者其他实惠的影响。他们大部分VIPs或者会员。他们不适用于降低了他们总体利润贡献的市场促销。相反,根据会员权益给予他们奖励。尽管有时候,这种奖励比市场促销还大,但这完全可控。
Actual Demand
Their demands of some comodities exist but is negatively correlated by price. It was widely represetned by Price Elasticity of Demand (PED) Demand, Wikipedia. Nowadays, more sophiticated Statistic based Machine Learning algorithm or Non-Data-Distribution-Dependant (N3D) algorithms produce more accurate results.
他们对商品的需求是存在的,但是受价格影响,成负相关。过去人们会用价格弹性系数(PED)Demand, Wikpedia,来表示这种关系。现在,更加精巧的基于统计的机器学习算法,和非数据假设分布依赖(N3D)的算法,可以产生更加准确的结果。
Latent Demand Business Dictionary
Latent demand comes from potential customers or potential desire from existing customers. They might not use or intend to use a commodity before. Cooresponding marketing campaign will give that commodity to users at a very competitive price or even for free to give the public some feeling that they might need it in the future. Such feeling or desire creates actual demands and some of them will be converted to rigid demands. It is the rigid demands that creates steady profits for a business.
潜在需求来自于潜在客户, 或者已经是客户的潜在欲望。他们可能从来没有使用,甚至计划使用一项商品。相应的市场推广计划,会用非常有竞争力的价格,甚至免费向用户推出商品,给他们一种未来他们会需要它的感觉。这种感觉或者欲望,创造出实际需求;其中一部分还会转化为刚需。正是刚需为商业提供了稳定的利润。
Membership
If customers have consistently regular needs over a commodity, they will be encouraged to be part of a long term membership plan. This is beneficial for both parties. Commodities providers will identify what features of a commodity a customer truely need. While, a member may gain some previlidges as a reward for their continuous contribution to the company’s profits.
如果客户对于商品有着持久的稳定的需求,他们会被鼓励成为长期客户计划的一部分。这对双方都有益。商品提供者可以甄别哪些产品特点是用户真正在意的;同时,因为他们持久的利润贡献,作为奖励,会员拥有一部分特权。
Asymmetric infomation
Based on previous research, in this post, asymmetric infomation is defined using conditional probability distribution (which can be learned from a specific model from statistic perspectives) so that we can express an “asynmmetric” concept in a model.
基于之前的研究,这篇博文里,非对称信息以条件概率的形式出现(可以从统计的角度学习)。这样,我们就可以在模型里面表达“非对称”的概念。
Assumption & notations
Here are notations for query $i$:
这里是请求$i$的符号:
- $q_{i}(u)$: a query $i$ from endpoint user $u$
- $I_{i}(v, k_{i}^{j}, u)$: marginal likelyhood user $u$ intent to purchase a specific commodity of value $v$, when $k_{i}^{j}$ $=$ deduction offered.
- $p(u)$: prior possibility user $u$ need the product.
- $Q$: totoal budget reserved for this market campaign.
- $d_{i}^{j}$: variable budget reserved from budegt $Q$ for query $i$
- $R_i(u)$: revenue user $u$ could contribute when he or she accepts some deduction offer. We wish that the generated $R_i$ coveres the budget fee at the end of a accounting period.
- $r_i$: ratio of deduction reserved from expected revenue
- $m_{i}(u)$: membership reward for query $i$
- $f_i(k_{i}^{j}, r_i)$: expected revenue for query i at deduction offer $k_{i}^{j}$
A customer who is in membership is assumed to pursue as much ratio of reward over their payment as possible given that they are smart poeple. The sad effect is that different services or priviledges can not be compared directly. As a result we need to convert them to accepted prices in market, so that we can compare. For example, different credit card memberships give you different abilities which can be purchased in the market.
假定会员消费者追求尽可能高的补贴比例, 如果他们是聪明人一定会这么做。糟糕的是,不同的会员服务,不能直接比较。因此我们将他们转换成市场行情下价格进行比较。比如,不同的信用卡提供会员增值的服务,这些服务也可以在市场上购买得到,因此消费者就大致对这个服务有了价值判断。
The existence of competitors in the market interferes market prices. It is possible to simulate multiple competitors in this area, however let us make things eaiser so that we can get some conclusion quickly without studying competitors behaviors.
竞争者的存在会干扰市场定价。在这个系统里模拟多竞争者的,是可能的。但是我们可以使事情简单一点,这样我们就可以快速得出结论,而不用考虑竞争者的行为。
System framework
The system is simple. The input is the union of logical conjunctions and commands constructed from bool expression, Indexing Boolean Expressions from user query. The output is either a price deduction proposal or a timeout span for the next proposal so that we can collect enough resources to negotiate with users.
The risk and secrets here are
- if a propsal is too low, we lose money; if the proposal is above what user can accpet, he or she will reject the proposal and wait for the next proposal,which increases our total time span for users to make decision
- if the total time span is too long for a user to make decision, he or she might quit the session. We deem this as being unsatisfied or equivently we lose a bounch money even if we sell nothing.
- if we losed too much money beyond the budget, we bankrupted.
系统不复杂。输入是”逻辑与”表达式的并集和命令,他们从用户查询的布尔表达式得来. 输出或者是一个价格折扣建议,或者是下一次折扣建议的定时器,我们将用它和用户“谈判”。
风险和秘密是:
- 如果建议价太低,我们损失金钱;如果建议价高过用户期望价,他可能会拒绝报价,并等待进入下一阶段谈判。这样会增加用户交易时间
- 如果用户交易时间太长,用户可能会退出谈判桌。我们认为,用户是不满意的,或者等价的我们损失了金钱(因为流失订单)
- 如果我们超出预算损失大量金钱, 就会破产(也许并没有真正破产,但这一阶段市场营销是失败的)。
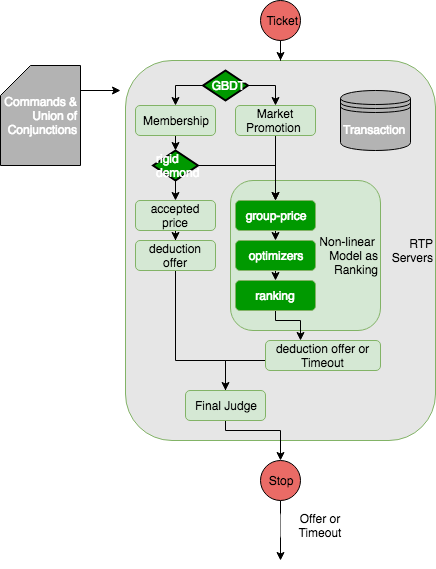
In first stage of model of RTP, a tree alike classification model like boosting tree is just good for inference. The detials will be disccused in Model Inference and Learning. A query will be forwarded to membership process line or marketing promotion by displaying process line, which depends on the demand detection results. The input is union of conjunction and commands detected; while the outputs are membership, groups, classified demands, and associated prices for the similar transactions.
RTP第一阶段,一个类似树的分裂模型就足够用于分类。细节会在模型推理和学习讨论。查询请求,根据需求分类,被转发到会员处理线,或者展示促销处理线。输入是“逻辑与”的并和检测出的命令;输出则是会员关系,用户分类,判定的需求,和相似交易记录的价格信息。
The reason why we use a model is here: in some comercial products, membership is sometimes implicit, the result of which depends on transaction history of a customer. We also need to compute exactly in which group a customer associated to the query belongs to and which demands the customer could possess. The tree model could be as simple as a thredshold for a specific data column. But it is not good for automation, because you should not push your AI engineers to repeat tedious computation again and again to verify the threshold used for classification, which is really boring and talents abusing. We prefer statistic based supervised or semi-supervised learning model over N3D model because inference in online process should be quick, agile, and tyipcal N3D algorithms is time consuming. Statistics based supervised or semi-supervised learning model also requires assumption that the data generated from the same distribution. If they were not, the cost function was wrong. Hence, the procedure is good for accuracy improvement.
我们这里使用模型理由是:在某些商业产品上,会员有时是隐含的。结果取决于历史交易信息。我们同时还需要计算,用户属于什么群体,需求是哪种类型。树形模型可以简单的如在某个数据列的条件阈值,但是这个对自动化过程并不好,因为你不能让你的AI工程师去重复计算一个条件阈值,这个相当无聊并浪费智力资源。相比较N3D算法,我们更喜欢基于统计的监督-半监督学习模型, 因为在线过程对实时性要求高,N3D算法通常比较慢。基于统计的监督、半监督学习模型还要求,数据来自于同一分布的假设,否则你的cost function就是错的。因此,这个过程有助于提高准确度。
It does not always mean that your are completely good here if you employ statistics based learning model for pre-cliassification. The statistic based learning model implies that you can be generally good as the average result (the medium result, the GBDT quantile result, etc. ) works as expected but not neccesarily good for a specific case. That is what a random variable means. To overcome uncertainty of a result produced by statistic based learning model, extra efforts needed. Negotiatin process is one of them to tackle the problem! This will be disscussed in Model Inference and Learning
采用了样本预分类学习模型并不意味着你完全正确。统计学习模型,意味着,大体上你是正确的,因为模型均值(中位数值,分位数值)达到了预期,但并不一定意味着,对于某个case,你是正确的。这就是随机变量的含义。为了克服不确定性,还需要采取额外的操作。“谈判”是其中一个方案!更多的信息,见模型推理和学习 or you might communicate with me directly!
The deduction offer will be derived from membership policies in the membership process line if we detect rigid demands.
如果我们检测到了“刚需”,会员线根据会员政策提供减免。
All the other cases will be forwared to Non-linear Optimization as Ranking, which is the most important part of the system. NOAR implements the most of logics to deliver an optimal deduction offer for users. If that is impossible, which is likely to happen in certain situations, we will give a timeout span.
其他情况,将被转发到非线性优化的排序形式处理。这里填写了NOAR的大量业务逻辑,去计算一个豁免最优值。如果最优解不可能,这在某些情况下非常可能,那么我们将给出一个等待时间区间(用于收集资源,重新评估)。
Finally, the systme makes the final judge over the offer proposal or a timeout span. We want to decide that:
- time span or priority number assigned to the customer in case that a customer rejects the offer (statistic optimal result does not mean accurate for this case )
- If the demand is the acutal demand and the customer is in membership, the final offer will be the comibnation of the two: $max(mem_offer,noar_offer)$.
最后系统将对Offer或者Timeout span给出最后裁定。我们需要决定
- 如果结果是用户拒绝豁免(统计最优结果,并不一定对个例准确),或者结果是Timeout span,我们需要计算用户等待时间,或者优先级
- 如果需求是实际需求,并且用户也是会员,那么豁免由两部分组成: $max(mem_offer,noar_offer)$
Objectives Analysis
The most of the most, we need to understand what result we want to achieve. This might be the most difficult part of a model. The well studied Google AdWords problem might be a good start point for this question.
重中之重是,我们需要我们需要达到什么的结果。这可能是RTP中最重要的部分。被很好研究的Google AdWords问题,可能是一个不错的开始。
The maximum expected revenue from query i is expressed as:
最大化查询i的收入这样表达:
where, big $I$ and $R$ are models database learned from data offline. $h$ is a transition function applied upon state data set.
$I$, $R$是线下训练成的模型库。$h$策略转移过程,作用在状态结果集上。
The equality is subjected to conditions:
受以下条件约束:
There are multiple interpretation of the $R_i$(trained offline, selected by online classification). Here is an example from latent demand to demonstrate its feasibility:
$R_i$是通过线下分类过程,线上快速查询,选出来的模型,有很多种意义。对潜在需求,有:
You might have never purchased a commodity. According to statistics within an accounting period T, 3 out of 10 people bought it buy it again. The average number of products people could buy is G. Hence $R_i$ $\approx$ $0.3v\frac{G}{T} dt$
Another example from actual demand:
你可能从未购买过一件商品。根据账期统计,大概3/10的人购买过它的人,会再次购买。人民购买的平均产品(算得)是G。因此,$R_i$ $\approx$ $0.3v\frac{G}{T} dt$
另外一个例子是,对于真实需求的:
You frequently purcahse a product on Monday eventing. For some unknown reason, you occasionally open an app to check real time price. Here is what you might think about: if the price falls below your expected price, you are going to purchase it, otherwise you try to negotiate with the servers or just give up withouting waiting for the next dudction offer proposal. In this case an indicator function might be empolyed.
Since $d_{i}^{j}$ affects intention people purchase a product, maximum of $f_i$ is classified as non-linear optimization problem. Of course $R$ and $I$ should be modeled in different process lines because they depend on different sampling data set. That will be solved by NOAR.
你可能会频繁在周一晚购买一件商品,
因为$d_{i}^{j}$影响人物购物意愿,最大化$f_i$被看做非线性优化。当然,他们由数据给出,$R$和$I$在不同的产品线上优化,因为他们依赖不同的采样数据。最后用NOAR来求解。
A market promotion compaign has two effects, as we have talked about, getting more customers in, getting less of them out. A market is successful iff sales from new customers can cover the budget and increase total revenue for a regular accounting period.
如前所述,市场营销活动,有两个效果:纳新和留存。该活动是成功的,当且仅当活动支出被预算覆盖,并且在一个账期内增加了对应的营收。
- If a demand is rigid demand which means $I_i$ is irrelevant with $k_i^j$, the market promotion keeps customers active by membership awards. Then $r_i$ is generated by Membership Policies for Mahcine(MPM).
- If a demand is actual demand, the market promotion encourages customers to complete payments of commodities to get inventory balence(or supply stable). More deduction $k_i^j$ means high $I_i$ and $b_i^j$ but lower profit and more revenue.
-
If a demand is latent demand, the market promotion intend to invite new customers in to use the products at the cost of market promotion budget $d_i^j$.
- 刚需意味着,$I_i$对折扣不敏感,市场营销利用会员奖励,来维持活跃度。$r_i$通过会员政策的机器语言来产生。
- 真是需求,意味着,市场营销鼓励参与者达成交易,从而保持仓储平衡(或者供应稳定). 更多的观测折扣$k_i^j$因为着更高的购物意愿和补贴,以及更少的利润更多的营收。
- 如果是潜在服务,市场营销,倾向于在预算范围内,邀请更多的用户使用、体验产品服务.
The good thing about above conditions is that AMM teams can setup multiple configuration files from online EXCEL application so that different cases is covered without touching underlying supervised learning model and they are easy to modify.
上述条件的好处是,敏捷市场管理团队,可以通过简单的操纵类似于Online Excel的应用程序,产生对应的配置文件,而不会修改底层的训练模型。
enum Demand{Rigid, Actual, Latent};
extern errorno;
int dispatch_lines(Request req) {
enum Demand demand = req.demand;
if (demand == UNDEF) {
errorno = INTERNAL_ERROR;
exit_proc("[proc_membership_line] demand is not defined.", errorno);
}
switch(demand) {
case Rigid:
proc_rigid__demand(req);
break;
case Actual:
proc_actual_demand(req);
break;
case Latent:
proc_latent_demand(req);
break;
default:
LOG.warn("Not implemented yet");
break
}
return 0;
}
...
There is a one basic problem for all of Non-convex optimization problems. Do you want to get the global optimium? If you cannot, local optimum is also accept as long as you can escape saddle pointsFaster Non-Convex Optimization Than SGD.
对于所有的非凸问题,有一个共同的困难是,如何得到全局最优?如果你不能的话,至少要规避saddle pointFaster Non-Convex Optimization Than SGD,从而,得到局部最优。
Morover, the optimization for sampling data does not garantee that each of the reuslt comes from the same hypothetic random variable distribution. Hence the best strategy we can employ is the heuristic method.
而且,采样优化也不能保证每一个结果都是来自于同一个假设随机变量的分布。因此最好的策略,还是启发性的方法。
If we have $f_i$ as f score for each of query, we also need $h$ as h score to evaluate how good our choice towards our targets: more money, more orders, less average waiting time: $g = f_i + h_i$. Buget works like a graph step jumping from one start point ($Q$) to the end point ($0$).
以图的角度来思考这个问题,如果我们已经有了f score,还需一个h score来评估,我们的选择到底对于达成我们的阶段目标有多大帮助:更多的金钱,更多的订单,更少的等待时间。每一次的预算补贴,类似,图中的一步:起始点是$Q$,终止点是$0$.
For example, if there are a lot of members queued waiting for servcies and our inventory is going to run out. Now one of customers who is not member querying for price, $h$ function might has dominate power to reject the detection offer issuing to force $d_i^j$ to be skipped.
比如,如果有很多人排队等待服务(超卖),而且我们的仓储也快耗尽了。现在有一个非会员顾客发出服务请求,$h$函数主导会拒绝提供营销补助。
How to evaluate our system?
If we cannot evaluate a method, we cannot imporve it - Peter Druker, The Master of Management
A/B test widely used for complex strategies verification. A winning A/B system will make sure that strategies are not correlated to each other. But it is still challenging for us to figure out how does our model affects company’s revenue.
A/B实验被广泛用于复杂策略验证。一个成功的A/B系统,应当可以确保,实验间的无关联性。但对我们来说,了解模型是如何影响公司效益是一件具有挑战的事情。
In general if your strategy help the company to gain more money steadily in A/B test, we say it works by help compoany to grow some percentage of renvenue. Because each step is measurable indicators (precision, cost fees, intention) we have general idea how does it work.
通常如果你的策略在A/B实验中,帮助公司稳定盈利,我们说它能够成功提高公司某些比例的收入。因为每一步都是可度量的指标(准确度,cost,购物意愿),我们大体上可以了解系统的工作原理。
Non-linear Optimzation as Ranking (NOAR)
The general ranking problems for a larget dataset is widely studied in commerail products. Both Promotion and optimization naturally gives a ranking if the targets can be converted to dicscret quantities. Since they work differently but can serve the same target, we have a choice to convet ML model to ranking and vera verse for our propomtion optmizers automata.
一般的大数据排序模型被广泛地在商业系统中研究、应用。如果它能转化为离散数值,折扣和优化天然地给出了一个目标的排序。因为优化和排序的工作原理不一样,必要的时候,我们可以互相转换。
Ranking problem as clissifcation was first introduced in around 2008 by Microsoft Research (MR). The classified favorable one has higher priority over the opposite. Finally they will form ranking from the positive and the negative classification.
排序用优化来解决,最早在2008年左右,由微软研究院发表。分类结果被分为正负样例,从而做出强弱排序。最终,全排序,通过局部排序得出。
Inspired by that, in NOAR, each Non-linear components are computed from ML models (whatever the algorithm you use). You continue the process until the objectives is in liear from, then we perform simplex rotation get find optimium in Big $O(n)$, where $n$ is the number of variables, then we get a table of appearances as the following
受到启发,在NORA里面,(正好相反),每一个非线性单元,都由一个模型给出(无所谓你用什么方法,都差不多),持续这个过程,直到所有非线性单元被模型替换掉。然后我们用凸点旋转类似的simplex算法,获得最优解。解的渐进复杂度和变量数量有关。
](/images/money/calipers.gif)
| $r_i$ | $d_i^j$ | $k_i^j$ | $R_i$ | $f_i$ | $h_i$ | $g$ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.8 | 30 | |||||
| 0.7 | 29 |
To obtain the optimum value of g and $<r_i, d_i^j, k_i^j>$, we just rank the results according to g and return the corresponding $<r_i, d_i^j, k_i^j>$ triple. Topk algorithm(I have a live example ready for use) preferred to be used here because, theoretically, price is not categorical value and can be converted into infinite segments, as a result of which your model bank grows accompanied with transaction continues.
要获得最优解$<r_i, d_i^j, k_i^j>$,我们需要对上面的表格进行排序。我们偏好使用Topk算法,因为理论上,价格非离散值,随着交易记录的积累,会被转换成无数个小区间。
Optimzers Automata (OA) and Automata Optimization (AO)
The most difficult part about Optimizers automata might be probablistic transition. The other part will be simply applied some of rules of our Membership Policies for Machine (MPM):
对于优化器自动机,最困难的地方应该是概率状态转移。其他部分将应用会员政策的机器语言规则:
Rule: “rule” ident “offer” Number Unit “deduct”
As long as each transition is unique (LL Language), we can apply gradient descent parsing directly without looking ahead recusively(stack).
只要状态转移时唯一的(LL Language),我们总能使用下降解析技术,而不必递归地向前“看”(栈)
The probablistic transition fucntion $h$ can be another ML model from data. For example, you can use spark in offline procedure to compute “provided that products supply is not enough, average time of people would likely to wait in a rainning night”. Then you can use that computed average waiting time to determine when $h$ transfer to $0$ or $v$ at the end the transition so that your prediction is much closer to the real situation.
概率转移函数$h$还可以是另外一个机器学习模型。比如,你线下利用spark得出,“如果产品供应不足,下雨天平均用户等等时间”,那你就可以用平均等待时间估算出平均谈判次数,并决定什么时候交易结束,$h$最后转移到$0$,或者$v$。这样的你的预测更准确点。
An automata can be optimized by reducing the transition steps. KMP, Boyer Moore are among the most effective automata optimization methods by trimming redundant searching branches and building a query table in advance. As Knuth taught us that do not overoptimize a system, we can carefully craft our OpDev system for us to summarize the optimization gradually that while collecting more and more user data.
通过减少转移步骤,可以优化自动机。KMP, Boyer Moore是最有效的优化自动机的技术之一。通过剪枝,提前构建转移查询表,我们可以提升速度。就像Knuth教导我们不要过度优化系统一样,我们仔细打造OptDev系统,并在收集数据的时候逐渐总结优化。
Model Inference and Learning
There are a lot of models inside the system served for different purposes. Hence little improvements of a model values a lot.
因为有比较多的模型在这个系统里面,为不同的目的服务,因此小小的改进意味着很多。
Feature
Research and contests in industries indicate that preprocessing of data plays a great role in the accuracy of ML models. A practical guide of data preprocessing or enhancement might be:
研究和竞赛表明,预处理数据在模型准度上非常重要。数据预处理和增强的一个实用引导,可以是:
- categorical value encoding: Discriminate and Non-Discriminate indexing. For labels or other similar categorical values, they are equal feature values. Onehot was employed as Non-discriminate encoder. However, if the cardinal of the feature values set is too larget, we need compress the length of onehot indexing. Word2vec is one of such compression algorithms which can hlep imporve accuracy and speed of training. However, sometimes, order natually gives importantce score, hence we need to use Discriminate indexing algorithmn by setting proper weights.
- Use factorization machine alike algorithms to produce feature basket encoding: combination of different categorical features give birth to new patterns. Such patterns was used in data mining system for products recommendation. Practices show that they help to improve scores
- Feature normalization might help: is you are using decision tree, normalization might not help, but it helps if you use DNN. You need to need try it.
-
stacked model as feature extractor: apply algorithms upon extracted features might imporve your scores.
- 离散值编码: 差别性,和费差别性编码。对于标签或者其他类似的离散值,他们是地位等同的特征值。Onehot曾经用来解决这个问题,但是如果特征值集基数太大,我们就需要压缩编码长度。Word2vec是其中一个这样的压缩算法可以加速训练,提高准确度。但是有时候,顺序天然地给出了重要性分数(一本书的章节),这时候我们就需要采用非差异化编码,并设定不同的权重
- 采用类似因子机一样的算法,计算特征购物篮编码: 不同离散值的组合会产生新的特征,这种特征曾经用在数据挖掘系统做推荐。实践表明他们有助提高得分
- 嵌套模型用于特征提取:在提起后的特征上执行算法,可能会提高你的得分
Samplings
The best you can learn from data is the sampling data distribution itself. You should keep your sampling algorithms effective so that your data itself reflects the law of nature.
能从数据学到的最好的东西,就是采样数据所代表的自然规律本身。因此,你需要保证你的采样算法有效地反应事实。
Learning
For algoithms training in a single machine, following commons might help.
对于大部分算法,以下方法是有效的:
- apply proximal gradients if neccesary: when parameters approaches points where no gradients numerically available, apply proximal gradients
- use linear search after several rounds of interation
-
run your algorithms multiple times using randomized initial weights might help to escape from saddle points
- 采用近似或者次梯度,如果必要的话:当参数解决一些数值上没有梯度的点,采用次梯度算法
- 几次迭代之后,做一次Line search
- 实验用随机的初始化的权重多跑几次,有助于逃离saddle points.
Future Work
Dual Channel Promotion strategies under Multiple Competitors
The question was recently arised in the public due to multiple competitors competition. The framework is good enough for AMM hence, operation team has ability to control market when competitors coming in. However this research does not cover how services suppliers affect the platform service provider.
这个问题因为多头竞争关系,最近被公众提出来。该算法框架可以应对敏捷市场管理,当竞争者出现,运营团队有一定的能力去控制市场。但是这个研究没有考虑到供应商如何影响平台(服务提供者).
Model Automata Error Chain Rule Study
Unlike Stacked Model, in which we can apply chain rule to deduce errors perturbation caused by input deviation, model Automata is much more complex. Autonomouse driving is also an Optimizers Automata, for example. To get a more accurate model, manufacturers and algroithms providers try to build a simulation engine so that we can control data flow in fine scale: if detection pefect -> how system works.
和嵌套模型不一样,我们可以通过链式法则,输入偏离引起的计算误差扰动,模型自动机非常复杂。比如,自动驾驶就是一个典型的模型自动机。为了获取更加准确的模型,主机厂商和算法供应商希望能够构建一个模拟引擎,可以更加细致地控制系统:比如完美感知下,系统是如何工作的。
Inspired by that, we can also build a simulation engine for RTP pressure testing machine: A virtual customer send a request (randomly sampled and twisted fom existing transaction database, we know the result of its negotiation), and inspect the computing process to find what happens to the system.
受此启发,我们希望构建一个RTP压力测试器:当虚拟顾客发送请求时候,(我们已经知道,谈判结果了,订单随机从数据选取),我们就可以监控计算过程,找出问题。
This should be mucher cheaper than AV research. Wish someday it comes into reality.
这可能比AV还简单。希望尽快成为现实。
Acknowledgement
Thanks for the all friends and mentors who support me along the way. The research was solely conducted by Lei (lwang11@mtu.edu) in 2016 - 2017 without holding interests in any agencies. It should not be used or implied to be used in any forms of IP including but not limited to social network media, software, without consent of Lei (lwang11@mtu.edu). All rights reserved.
Thanks for the Help from doctor (candidate) Hanzhang Qin & editor 留德华叫兽 (nickname from Chinese online discussion community Zhihu) on publishing. (updated on May 13th 2018)
Bibliography
- XIAO,Jian, DAN Bin, ZHANG Xu-mei, Study on cooperation strategy between electronic channels and retailers in dual-channel supply chain , Chongqing University, Journal of Sysems Engineering, doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-5781.2009.06.006
- H. S. Ahn, I. Duenyas, R. Q. Zhang, Price competition between retailers and manufacturer-owned stores, University of California at Berkeley Working paper, 2002
- http://www.businessdictionary.com/definition/latent-demand.html
- P. Li, Christopher J.C Burges and Qiang Wu, Learning to Rank Using Classification and Gradient Boosting, 2008, Micorsoft Research
- WHANG S. E., MOLINA H. G., Indexing Boolean Expression.[C]. Proceeding of VLDB,2009. 2(1).
- ZOBEL J., MOFFAT A., Iverted Files For Text Search Engines[J]. ACM Computing Surveys, 2006, 38(4)
- Natasha 2: Faster Non-Convex Optimization than SGD - How to Swing by Saddle Points, third-version, Zeyuan Allen-Zhu, August 28 2017, Micorsoft Research, Redmond, arXiv:1708.08694v3.
- http://www-cgrl.cs.mcgill.ca/~godfried/research/calipers.html
- http://scikit-learn.org/stable/modules/preprocessing.html#encoding-categorical-features